Firebug and FirePath add-ons of Firefox browser are playing major role to get the XPath and CSS path of any element easily and quickly. Earlier we learnt how to use firebug and firepath add-on with Firefox browser to get XPath or CSS of any element In THIS POST. Now supposing I need both. Edit Firefox was installed by automation developers only to get xpath /locator from it, When firepath stopped its development many people scared to update their firefox versions. Now people are happy as they have got alternative. Chropath's unique feature now seems better than firepath. 'There is alternative for everything if not, lets create. There are three methods that you could use to invoke Firebug and Firepath in Firefox. Click on the Firebug icon on the top right corner of the page. Press F12 from your keyboard when the Firefox browser is active. Click on the View icon on the top of the Firefox browser and select Firebug. Firebug and Firepath addon’s not compatible with new version of firefox. Caitmuenster (Caitlin Neiman) 22 November 2017 18:02 #2 Firebug has been retired (see Saying Goodbye to Firebug). XPIs can be downloaded in another way as well. 1) Go to FirePath XPI download page. Right click on ‘Add to Firefox‘ and select ‘Save AS.‘ to save the XPI of the FirePath. How to Add Extensions (Firebug & FirePath) to FirefoxDriver? Time to load the saved extensions to FireFoxDriver.
Install FireBug Addon for Firefox
Firebug (Firefox Add-on) is a web development tool that facilitates the debugging, editing and monitoring of any website’s CSS, HTML, DOM and JavaScript. In Selenium, Firebug is used to inspect the UI elements of the web application under test.
How to Install Firebug ?
Please follow the below steps for installing the Firebug Addon for Firefox Browser:
- Verify that a Firefox is instead in your system else download it from http://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/new/ and read the version of the Browser from About Firefox in Help menu.
- Launch the Firefox Browser and browse for https://getfirebug.com/downloads . Then, select the Stable FireBug version which is compatible with your Firefox Browser version installed in Step#3 and click on ‘Download’ link
- Ensure that Firefox ADD-ONS page is displayed with ‘FireBug’ add-on and click on ‘Add to Firefox’ button to install the ‘FireBug’ add-on.
4. Click on ‘Install Now’ button on the displayed Popup Window.
5. After Installation restart (i.e. close and reopen) the Firefox Browser.
6. Ensure that FireBug icon is displayed on the FireFox Browser Window as shown in the below screenshot:
Firepath Addon for Firefox
Before explaining how to install Firepath, I would like to explain why Firepath is used in Selenium Test Automation. Firepath is used to create the CSS and XPath locators to locate the UI elements of the Web Application Under Test.
How to Install Firepath ?
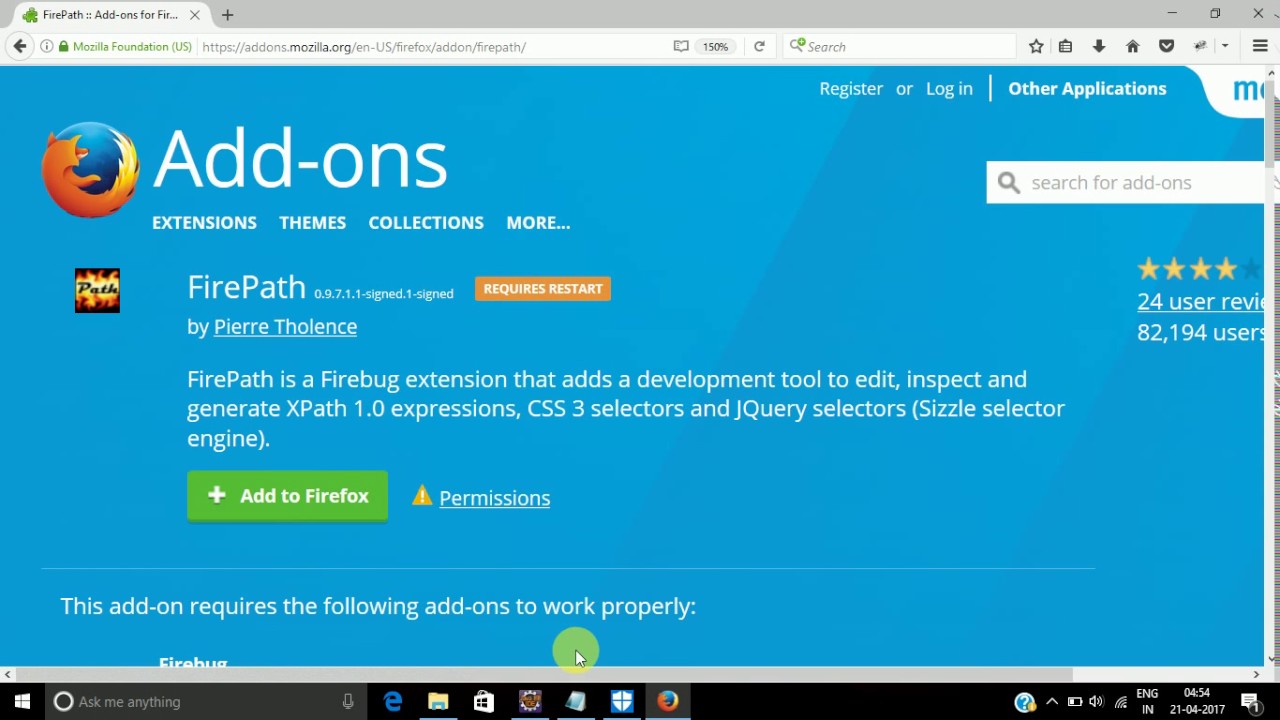
1. Open Firefox browser and access https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/firepath/2. Ensure that Firefox Add-ons page is displayed with Firepath Add-on
3. Click on ‘Add to Firefox’ Button to download the Firepath Add-on
4. Ensure that a Popup dialog is displayed and click on ‘Install Now’ button on the displayed dialog
5. Restart (i.e. Close and Reopen) the Firefox Browser after Firepath is installed
6. Click on FireBug icon on the top right side of the page as shown below:
7. Ensure that Firepath tab is now displayed in the FireBug interface after installing Firepath as shown below:
Firebug Addon Download
How to use FireBug and Firepath
1. Launch Firefox Browser and browse any site say www.google.com
2. Press F12 key or click on the ‘FireBug’ icon on the Firefox Browser
3. Ensure that the FireBug options gets displayed as shown below
4. Click on the ‘Inspect Element’ option of the FireBug as shown below, select any UI element on the page say ‘Google Logo’ and ensure that the source code of the selected UI element (i.e. Google Logo in this example) is highlighted as shown below
5. Observe that the above highlighted source code is in html format. We may need this source code to identify the properties of the selected UI element (i.e. Google Logo in this example)
6. For example if we want to know the id property details of the selected UI element Google Logo. First we need to inspect the Google Logo by following the above 4 steps and copy the ‘id’ details from the highlighted source code as shown below7. Click on the ‘Firepath’ tab to find out the Xpath value of the inspected element (i.e. Google Logo in this example) as shown below:
8. Ensure that ‘Xpath’ property value of the selected UI element (i.e. Google Logo) is displayed by default as shown below:
9. Click on the Dropdown field as shown below and select ‘CSS’
10. Ensure that ‘CSS’ property value of the inspected UI element (i.e. Google Logo) is displayed as shown belowFirefox Developer Tools is a set of web developer tools built into Firefox. You can use them to examine, edit, and debug HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
This section contains detailed guides to all of the tools as well as information on how to debug Firefox for Android, how to extend DevTools, and how to debug the browser as a whole.
If you have any feedback on DevTools or want to contribute to the project, you can join the DevTools community.
Note: If you are just getting started with web development and using developer tools, our learning docs will help you — see Getting started with the Web and What are browser developer tools? for good starting points.
The Core Tools
You can open the Firefox Developer Tools from the menu by selecting Tools > Web Developer > Toggle Tools or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + I or F12 on Windows and Linux, or Cmd + Opt + I on macOS.
The ellipsis menu on the right-hand side of Developer Tools contains several commands that let you perform actions or change tool settings.
| This button only appears when there are multiple iframes on a page. Click it to display a list of the iframes on the current page and select the one with which you want to work. |
| Click this button to take a screenshot of the current page. (Note: This feature is not turned on by default and must be enabled in settings before the icon will appear.) |
| Toggles Responsive Design Mode. |
| Opens the menu that includes docking options, the ability to show or hide the split console, and Developer Tools settings. The menu also includes links to the documentation for Firefox Web Tools and the Mozilla Community. |
| Closes the Developer Tools |
Page Inspector
View and edit page content and layout. Visualize many aspects of the page including the box model, animations, and grid layouts.
Web Console
See messages logged by a web page and interact with the page using JavaScript.
Firepath Plugin For Firefox
JavaScript Debugger
Stop, step through, examine, and modify the JavaScript running on a page.
Network Monitor
See the network requests made when a page is loaded.
Performance Tools
Analyze your site's general responsiveness, JavaScript, and layout performance.
Responsive Design Mode
Firebug Add On Firefox
See how your website or app will look and behave on different devices and network types.
Accessibility inspector
Provides a means to access the page's accessibility tree, allowing you to check what's missing or otherwise needs attention.
Application panel
Provides tools for inspecting and debugging modern web apps (also known as Progressive Web Apps). This includes inspection of service workers and web app manifests.
Note: The collective term for the UI inside which the DevTools all live is the Toolbox.
More Tools
These developer tools are also built into Firefox. Unlike the 'Core Tools' above, you might not use them every day.
- Memory
- Figure out which objects are keeping memory in use.
- Storage Inspector
- Inspect cookies, local storage, indexedDB, and session storage present in a page.
- DOM Property Viewer
- Inspect the page's DOM properties, functions, etc.
- Eyedropper
- Select a color from the page.
- Style Editor
- View and edit CSS styles for the current page.
- Taking screenshots
- Take a screenshot of the entire page or of a single element.
- Measure a portion of the page
- Measure a specific area of a web page.
- Rulers
- Overlay horizontal and vertical rulers on a web page
For the latest developer tools and features, try Firefox Developer Edition.
Connecting the Developer Tools
If you open the developer tools using keyboard shortcuts or the equivalent menu items, they'll target the document hosted by the currently active tab. But you can attach the tools to a variety of other targets, too, both within the current browser and in different browsers or even different devices.
- about:debugging
- Debug add-ons, content tabs, and workers running in the browser.
- Connecting to Firefox for Android
- Connect the developer tools to an instance of Firefox running on an Android device.
- Connecting to iframes
- Connect the developer tools to a specific iframe in the current page.
- Connecting to other browsers
- Connect the developer tools to Chrome on Android and Safari on iOS.
Debugging the browser
By default, the developer tools are attached to a web page or web app. But you can also connect them to the browser as a whole. This is useful for browser and add-on development.
- Browser Console
- See messages logged by the browser itself and by add-ons, and run JavaScript code in the browser's scope.
- Browser Toolbox
- Attach the Developer Tools to the browser itself.
Extending DevTools
For information on extending the Firefox DevTools, see Extending the developer tools over in the Browser Extensions section of MDN.
Migrating from Firebug
Firebug has come to the end of its lifespan (see Firebug lives on in Firefox DevTools for details of why), and we appreciate that some people will find migrating to another less familiar set of DevTools to be challenging. To ease a transition from Firebug to the Firefox developer tools, we have written a handy guide — Migrating from Firebug.
Contribute
If you want to help improve the developer tools, these resources will get you started.
- Get Involved
- Our community website explains how to get involved.
- bugs.firefox-dev.tools
- A tool helping to find bugs to work on.